Page 69 - CARILEC CE Industry Journal_Oct_2019
P. 69
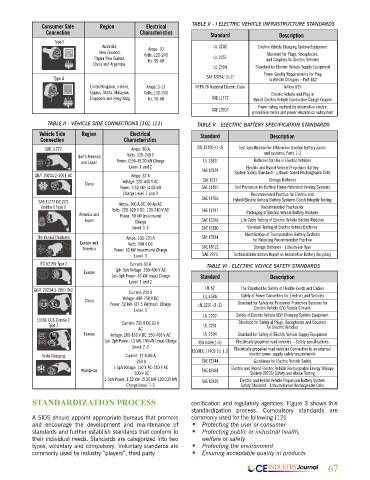
Consumer Side Region Electrical TABLE II - I ELECTRIC VEHICLE INFRASTRUCTURE STANDARDS
Connection Characteristics Standard Description
Type I
Australia, Amps: 10 UL 2202 Electric Vehicle Charging System Equipment
New Zealand, Standard for Plugs, Receptacles,
Papua New Guinea, Volts: 120-240 UL 2251 and Couplers for Electric Vehicles
China and Argentina. Hz: 50-60
UL 2594 Standard for Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment
Power Quality Requirements for Plug
Type G SAE J2894/ (1-2) In Vehicle Chargers - Part 1&2
United Kingdom, Ireland, Amps: 3-13 NFPA 70 National Electric Code Article 625
Cyprus, Malta, Malaysia, Volts: 110-240 Electric Vehicle and Plug in
Singapore and Hong Kong Hz: 50-60 SAE J1772 Hybrid Electric Vehicle Conductive Charge Coupler
Power rating method for automotive electric
SAE J2907 propulsion motor and power electronics subsystem
TABLE II - VEHICLE SIDE CONNECTIONS [10], [11] TABLE V - ELECTRIC BATTERY SPECIFICATION STANDARDS
Vehicle Side Region Electrical Standard Description
Connection Characteristics
SAE J1772 Amps: 80 A ISO 12405-(1-3) Test specification for lithium-ion traction battery packs
and systems: Parts 1-3
North America Volts: 120-240 V
and Japan Power: 0.96-19.20 kW Charge UL 2580 Batteries for Use in Electric Vehicles
Level: 1 and 2 Electric and Hybrid Vehicle Propulsion Battery
SAE J2929 System Safety Standard - Lithium-based Rechargeable Cells
GB/T 20234.2-2011 AC Amps: 32 A
China Voltage: 220-440 V AC SAE J537 Storage Batteries
Power: 3.52 kW-14.08 kW SAE J1495 Test Procedure for Battery Flame Retardant Venting Systems
Charge Level: 1 and 2 Recommended Practice for Electric and
SAE J1766
SAE J1772 DC CCS Amps: 200 A DC, 80 An AC Hybrid Electric Vehicle Battery Systems Crash Integrity Testing
Combo 1 Type 1 Volts: 200-600 V DC, 120-240 V AC SAE J1797 Recommended Practice for
America and Power: 90 kW (maximum) Packaging of Electric Vehicle Battery Modules
Japan Charge SAE J2288 Life Cycle Testing of Electric Vehicle Battery Modules
Level: 1-3 SAE J2380 Vibration Testing of Electric Vehicle Batteries
Identification of Transportation Battery Systems
The Yazaki Chademo Amps: 100-120 A SAE J2984 for Recycling Recommended Practice
Europe and Volts: 500 V DC
America Power: 60 kW (maximum) Charge SAE J3012 Storage Batteries - Lithium-ion Type
Level: 3 SAE 2974 Technical Information Report on Automotive Battery Recycling
IEC 62196 Type 2 Current: 63 A TABLE VI - ELECTRIC VEHICE SAFETY STANDARDS
Europe 1ph-3ph Voltage: 250-400 V AC
1ph-3ph Power: 43 kW (max) Charge Standard Description
Level: 1 and 2
GB/T 20234.3-2011 DtC Current: 250 A UL 62 The Standard for Safety of Flexible Cords and Cables
China Voltage: 400-750 V DC UL 458A Safety of Power Converters for Electric Land Vehicles
Power: 50 kW-187.5 kW(max), Charge UL 2231-(1-2) Standard for Safety for Personnel Protection Systems for
Level: 3 Electric Vehicle (EV) Supply Circuits
UL 2202 Safety of Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging System Equipment
EU DC CCS Combo 2 Standard for Safety of Plugs, Receptacles and Couplers
Type 2 Current: 200 A DC,63 A UL 2251 for Electric Vehicles
AC
Europe Voltage: 200-850 V DC, 250-400 V AC UL 2594 Standard for Safety of Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment
1ph-3ph Power: 13 kW-170 kW (max) Charge ISO 6469(1-3) Electrically propelled road vehicles – Safety specifications
Level: 2-3
ISO/IEC 17409 Ed. 1.0 Electrically propelled road vehicles Connection to an external
Tesla Charging Current: 12 A-80 A electric power supply safety requirements
-250 A SAE J2344 Guidelines for Electric Vehicle Safety
1-3ph Voltage: 110 V AC-240 V AC
Worldwide SAE J2464 Electric and Hybrid Electric Vehicle Rechargeable Energy Storage
- 500 V DC System (RESS) Safety and Abuse Testing
1-3ph Power: 1.32 kW-19.26 kW-120/135 kW SAE J2929 Electric and Hybrid Vehicle Propulsion Battery System
Charge Level: 1-3 Safety Standard - Lithium-based Rechargeable Cells
STANDARDIZATION PROCESS certification and regulatory agencies. Figure 3 shows this
standardization process. Compulsory standards are
A SIDS should appoint appropriate bureaus that promote commonly used for the following [12]:
and encourage the development and maintenance of • Protecting the user or consumer
standards and further establish standards that conform to • Protecting public or industrial health,
their individual needs. Standards are categorized into two welfare or safety
types, voluntary and compulsory. Voluntary standards are • Protecting the environment
commonly used by industry “players”, third party • Ensuring acceptable quality in products
CE INDUSTRY Journal 67