Page 28 - CE_Industral_Journal_2014
P. 28
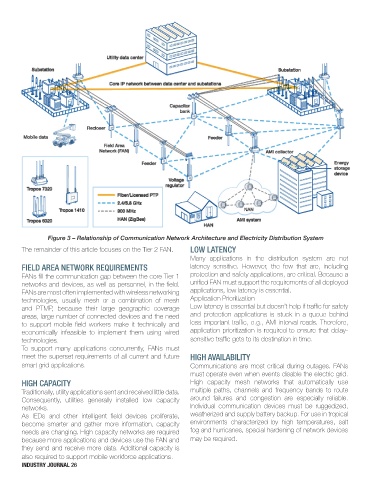
Figure 3 – Relationship of Communication Network Architecture and Electricity Distribution System
The remainder of this article focuses on the Tier 2 FAN. LOW LATENCY
Many applications in the distribution system are not
FIELD AREA NETWORK REQUIREMENTS latency sensitive. However, the few that are, including
FANs fill the communication gap between the core Tier 1 protection and safety applications, are critical. Because a
networks and devices, as well as personnel, in the field. unified FAN must support the requirements of all deployed
FANs are most often implemented with wireless networking applications, low latency is essential.
technologies, usually mesh or a combination of mesh Application Prioritization
and PTMP, because their large geographic coverage Low latency is essential but doesn’t help if traffic for safety
areas, large number of connected devices and the need and protection applications is stuck in a queue behind
to support mobile field workers make it technically and less important traffic, e.g., AMI interval reads. Therefore,
economically infeasible to implement them using wired application prioritization is required to ensure that delay-
technologies. sensitive traffic gets to its destination in time.
To support many applications concurrently, FANs must
meet the superset requirements of all current and future HIGH AVAILABILITY
smart grid applications. Communications are most critical during outages. FANs
must operate even when events disable the electric grid.
HIGH CAPACITY High capacity mesh networks that automatically use
Traditionally, utility applications sent and received little data. multiple paths, channels and frequency bands to route
Consequently, utilities generally installed low capacity around failures and congestion are especially reliable.
networks. Individual communication devices must be ruggedized,
As IEDs and other intelligent field devices proliferate, weatherized and supply battery backup. For use in tropical
become smarter and gather more information, capacity environments characterized by high temperatures, salt
needs are changing. High capacity networks are required fog and hurricanes, special hardening of network devices
because more applications and devices use the FAN and may be required.
they send and receive more data. Additional capacity is
also required to support mobile workforce applications.
INDUSTRY JOURNAL 26