Page 29 - CE_Industral_Journal_2014
P. 29
SCALABLE FLEXIBLE
Field area networks must scale to cover large geographic To support the widest variety of applications and devices,
areas, potentially the utility’s entire service territory. They the FAN must be built on industry standards such as
must also scale to support, directly or via NANs, millions TCP/UDP/IP, 802.11 (Wi-Fi) and 802.3 (Ethernet). To best
of connected devices. At the same time, because utilities integrate legacy field devices and avoid stranded assets,
may choose to roll out their smart grids incrementally, the the FAN must also support secure network connections
FAN must be economical to implement on a small scale,
say at a single substation or along a single feeder. to devices that use serial links and automation protocols.
SECURE MOBILITY
As utilities adopt IP in field area networks, fear of cyber- Providing communications for field crews requires that the
attacks increases. However, IP-based architectures also FAN support mobility.
bring security advantages. The tools used to thwart cyber-
attacks in enterprise networks have been honed for years FIELD AREA COMMUNICATION NETWORK
and are constantly being updated. Enterprise security TECHNOLOGY CHOICES
tools that should be leveraged in FANs include IPsec virtual As shown in Figure 4, numerous wireless technology
private networks (VPNs), firewalls, RADIUS authentication choices exist for implementing FANs. However, when the
and AES encryption. characteristics of these technologies are compared to
FAN requirements, broadband wireless mesh networks,
supplemented by PTMP links when needed, best meet
the requirements.
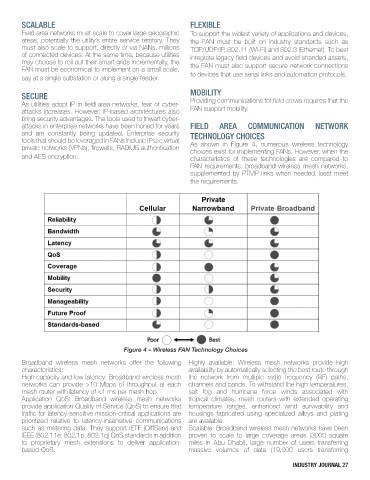
Figure 4 – Wireless FAN Technology Choices
Broadband wireless mesh networks offer the following Highly available: Wireless mesh networks provide high
characteristics: availability by automatically selecting the best route through
High capacity and low latency: Broadband wireless mesh the network from multiple radio frequency (RF) paths,
networks can provide >10 Mbps of throughput at each channels and bands. To withstand the high temperatures,
mesh router with latency of <1 ms per mesh hop. salt fog and hurricane force winds associated with
Application QoS: Broadband wireless mesh networks tropical climates, mesh routers with extended operating
provide application Quality of Service (QoS) to ensure that temperature ranges, enhanced wind survivability and
traffic for latency-sensitive mission-critical applications are housings fabricated using specialized alloys and plating
prioritized relative to latency-insensitive communications are available.
such as metering data. They support IETF (DiffServ) and Scalable: Broadband wireless mesh networks have been
IEEE (802.11e, 802.1p, 802.1q) QoS standards in addition proven to scale to large coverage areas (3000 square
to proprietary mesh extensions to deliver application- miles in Abu Dhabi), large number of users transferring
based QoS. massive volumes of data (19,000 users transferring
INDUSTRY JOURNAL 27