Page 36 - CE_Industral_Journal_2014
P. 36
Introduction of an Easy Method to
Analyze the Inuence of CT Saturation
on the Protection System
Eugenio Carvalheira
INTRODUCTION transient CT saturation will occur for given burden and
Almost all protective relays used in power systems rely fault conditions [1], but this does not help much if for the
on phase current information for their operation, typically above-mentioned reasons CTs are (or have to be) chosen
provided by the secondary winding of conventional current that will saturate under adverse conditions. The question
transformers (CTs). Although several modern alternatives is: How will the connected relays cope with these non-
to iron-core CTs exist (e.g. Rogowski coil, several other ideal signals? Can a certain amount of saturation be
approaches to unconventional transformers) the iron- acceptable, i.e. will the relay still trip with acceptable trip
core type is by far the most common. Due to commercial time and reach tolerance under all realistic fault conditions?
or space limitations, CTs are often selected for proper
steady-state current replication but with little reserves APPROACH
regarding transient fault conditions. Thus the primary- A proper assessment of the reliability of the protection
side sine-shape currents with a transient DC component performance in case of actually possible CT saturation is
during fault occurrence may result in secondary distortion only possible by considering all relevant conditions of the
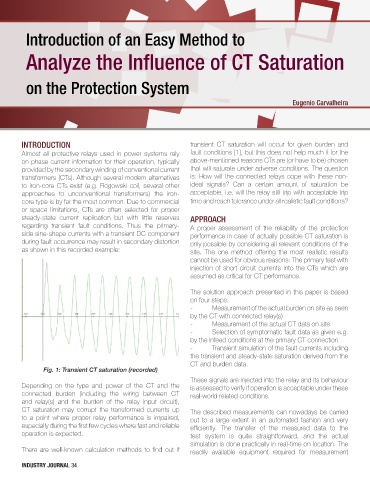
as shown in this recorded example: site. The one method offering the most realistic results
cannot be used for obvious reasons: The primary test with
injection of short circuit currents into the CTs which are
assumed as critical for CT performance.
The solution approach presented in this paper is based
on four steps:
- Measurement of the actual burden on site as seen
by the CT with connected relay(s)
- Measurement of the actual CT data on site
- Selection of symptomatic fault data as given e.g.
by the infeed conditions at the primary CT connection
- Transient simulation of the fault currents including
the transient and steady-state saturation derived from the
CT and burden data.
Fig. 1: Transient CT saturation (recorded)
These signals are injected into the relay and its behaviour
Depending on the type and power of the CT and the is assessed to verify if operation is acceptable under these
connected burden (including the wiring between CT real-world related conditions.
and relay(s) and the burden of the relay input circuit),
CT saturation may corrupt the transformed currents up The described measurements can nowadays be carried
to a point where proper relay performance is impaired, out to a large extent in an automated fashion and very
especially during the first few cycles where fast and reliable efficiently. The transfer of the measured data to the
operation is expected. test system is quite straightforward, and the actual
simulation is done practically in real-time on location. The
There are well-known calculation methods to find out if readily available equipment required for measurement
INDUSTRY JOURNAL 34