Page 56 - CARILEC CE Industry Journal_Oct_2019
P. 56
Figure 14 represents a normal Pressure-Volume or PV
Curve. The PV is used to calculate the Indicated
Horsepower (IHP) and Indicated Mean Effective
Pressure (IMEP).
Fig. 14 - Pressure Volume Curve
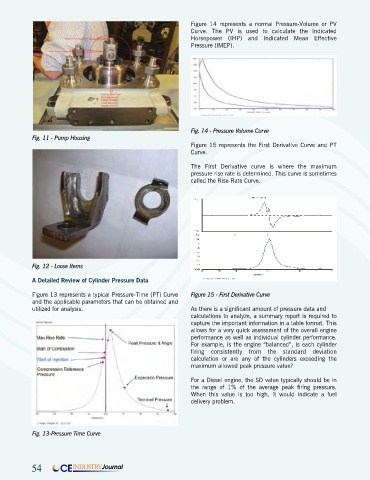
Fig. 11 - Pump Housing
Figure 15 represents the First Derivative Curve and PT
Curve.
The First Derivative curve is where the maximum
pressure rise rate is determined. This curve is sometimes
called the Rise-Rate Curve.
Fig. 12 - Loose Items
A Detailed Review of Cylinder Pressure Data
Figure 13 represents a typical Pressure-Time (PT) Curve Figure 15 - First Derivative Curve
and the applicable parameters that can be obtained and
utilized for analysis. As there is a significant amount of pressure data and
calculations to analyze, a summary report is required to
capture the important information in a table format. This
allows for a very quick assessment of the overall engine
performance as well as individual cylinder performance.
For example, is the engine “balanced”, is each cylinder
firing consistently from the standard deviation
calculation or are any of the cylinders exceeding the
maximum allowed peak pressure value?
For a Diesel engine, the SD value typically should be in
the range of 1% of the average peak firing pressure.
When this value is too high, it would indicate a fuel
delivery problem.
Fig. 13-Pressure Time Curve
54 CE INDUSTRY Journal