Page 25 - CE_Industral_Journal_2015
P. 25
Oil reclamation is a process that removes oxidation products to its aniline point, the acid and sludge begin to leach out of
and contaminants from the fluid which occur due to aging of the paper insulation. The acid and sludge are then removed
the transformer. The contaminants include various oxidation from the oil when the oil is pumped through a special
decay products, such as acid and sludge, and material from granular filtering medium.
the cellulose insulation and support structure used in the
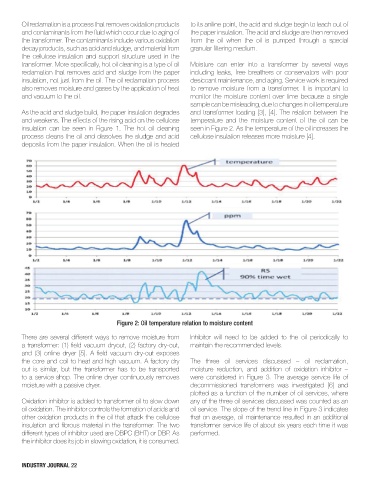
transformer. More specifically, hot oil cleaning is a type of oil Moisture can enter into a transformer by several ways
reclamation that removes acid and sludge from the paper including leaks, free breathers or conservators with poor
insulation, not just from the oil. The oil reclamation process desiccant maintenance, and aging. Service work is required
also removes moisture and gases by the application of heat to remove moisture from a transformer. It is important to
and vacuum to the oil. monitor the moisture content over time because a single
sample can be misleading, due to changes in oil temperature
As the acid and sludge build, the paper insulation degrades and transformer loading [3], [4]. The relation between the
and weakens. The effects of the rising acid on the cellulose temperature and the moisture content of the oil can be
insulation can be seen in Figure 1. The hot oil cleaning seen in Figure 2. As the temperature of the oil increases the
process cleans the oil and dissolves the sludge and acid cellulose insulation releases more moisture [4].
deposits from the paper insulation. When the oil is heated
Figure 2: oil temperature relation to moisture content
There are several different ways to remove moisture from Inhibitor will need to be added to the oil periodically to
a transformer: (1) field vacuum dryout, (2) factory dry-out, maintain the recommended levels.
and (3) online dryer [5]. A field vacuum dry-out exposes
the core and coil to heat and high vacuum. A factory dry The three oil services discussed – oil reclamation,
out is similar, but the transformer has to be transported moisture reduction, and addition of oxidation inhibitor –
to a service shop. The online dryer continuously removes were considered in Figure 3. The average service life of
moisture with a passive dryer. decommissioned transformers was investigated [6] and
plotted as a function of the number of oil services, where
Oxidation inhibitor is added to transformer oil to slow down any of the three oil services discussed was counted as an
oil oxidation. The inhibitor controls the formation of acids and oil service. The slope of the trend line in Figure 3 indicates
other oxidation products in the oil that attack the cellulose that on average, oil maintenance resulted in an additional
insulation and fibrous material in the transformer. The two transformer service life of about six years each time it was
different types of inhibitor used are DBPC (BHT) or DBP. As performed.
the inhibitor does its job in slowing oxidation, it is consumed.
industry Journal 22